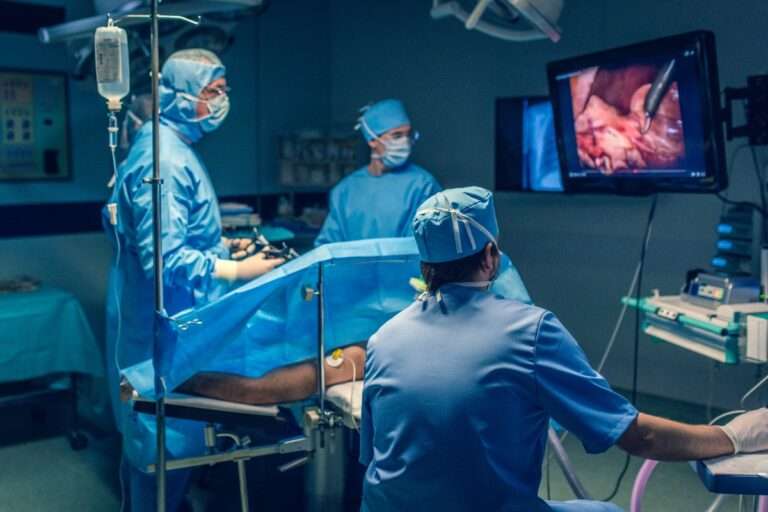
Laparoscopic Myomectomy is the surgical removal of uterine fibroids while leaving the uterus intact. It is the primary treatment option for patients who still want to conceive or prefer not to have a hysterectomy through a minimally invasive procedure in which small incisions are made in the abdomen over the fibroid’s location. A camera and surgical instruments are inserted through these incisions to visualize and act on the uterus.
The symptoms of uterine fibroids differ depending on their size, location in the uterus, and type. They are most commonly found in menstruating women between the ages of 30 and 50.
There is no link between birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy used to treat menopause and uterine fibroids. When compared to women with normal blood pressure, certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, may increase the risk of uterine fibroids by 24%.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of uterine fibroids is
Diagnosis
Treatment