What is Endometriosis?
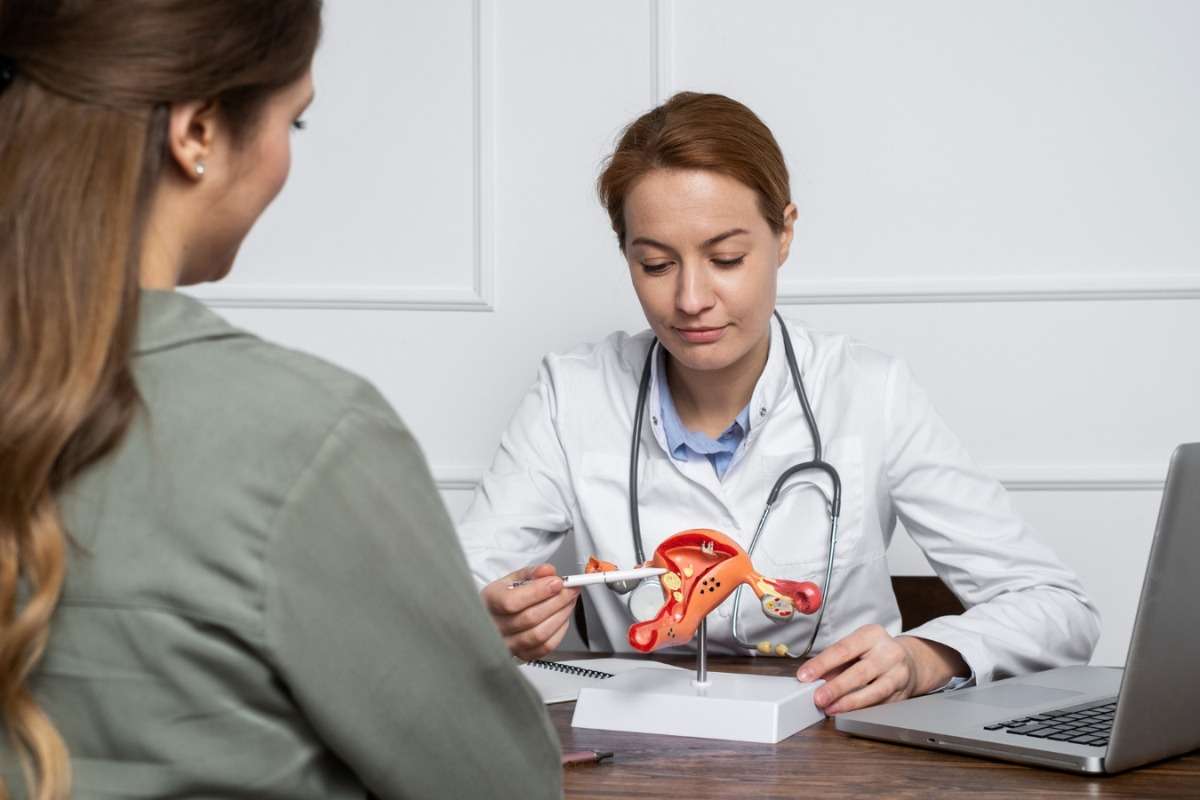
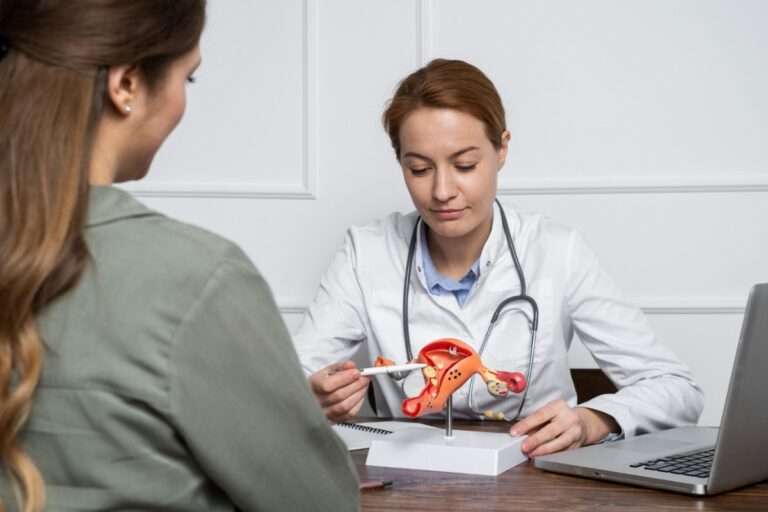
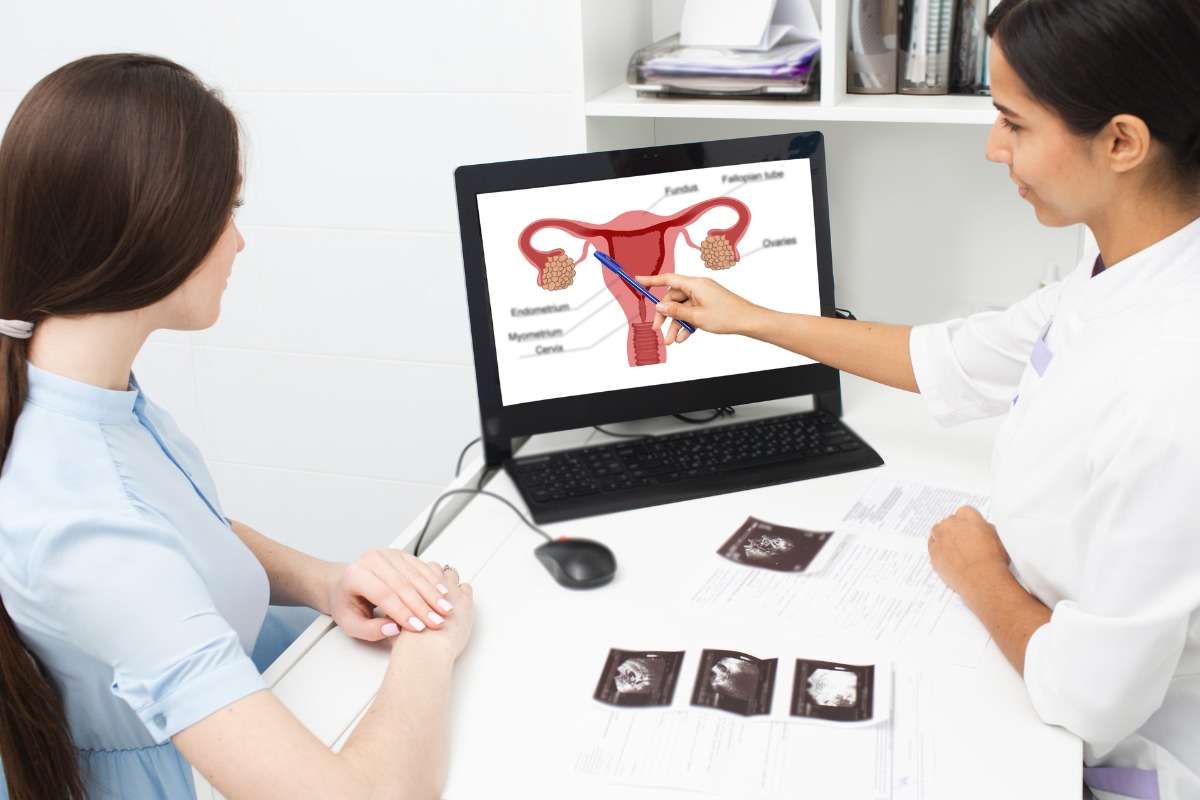
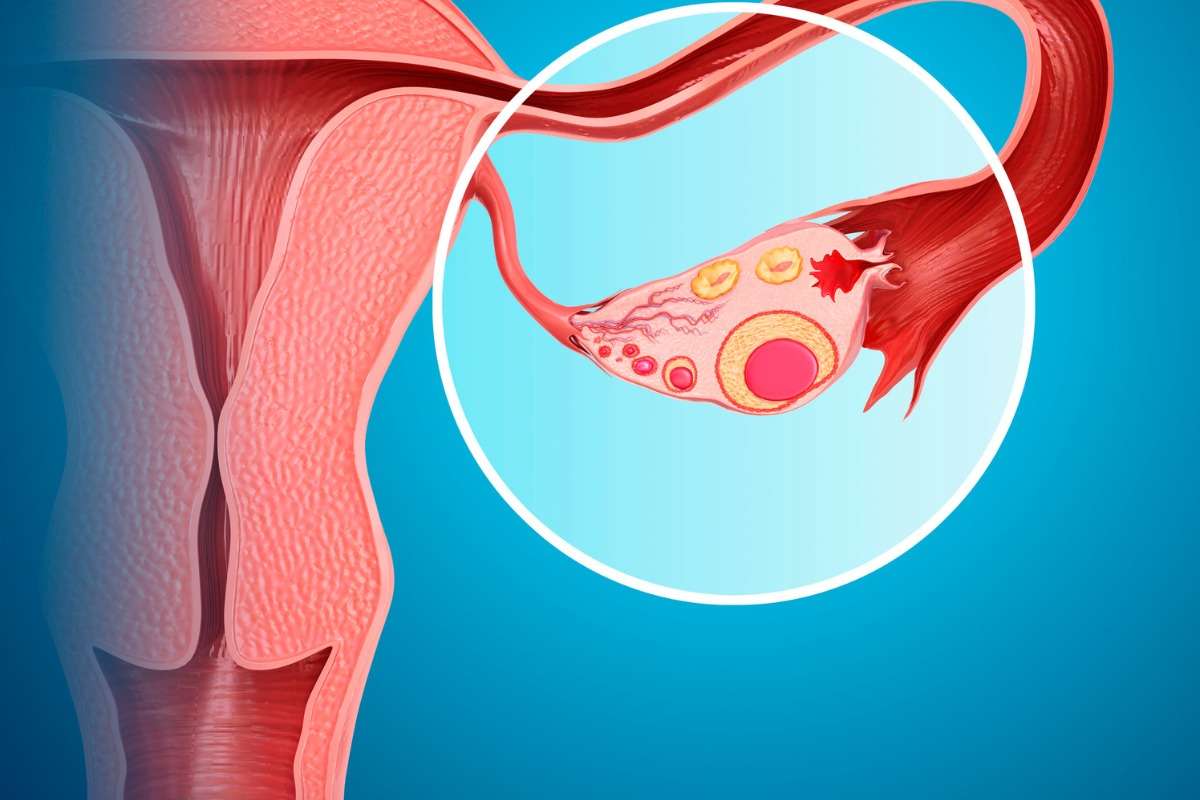
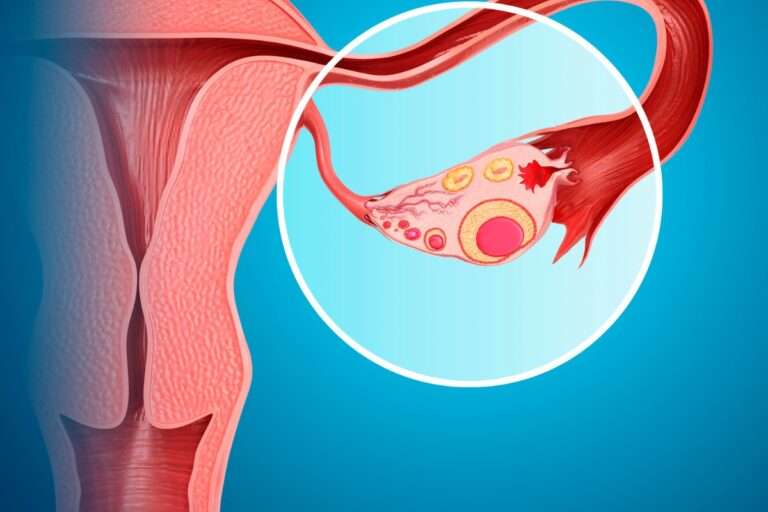
Endometriosis is a disorder in which the endometrium (the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus or womb) develops outside of the uterus or womb.
Endometriosis most commonly affects the lower abdomen and pelvis, however, it can appear anywhere in the body.
As a result, the normal tissue surrounding the endometriosis implants becomes irritated, swells, and has scars.
During their reproductive years, almost 10% of women suffer from this illness.
Most common symptoms are:
- Menstrual cramps that are too severe.
- Menstrual flow that is abnormal or excessive.
- Urination is painful during menstruation.
- Intercourse discomfort.
- Menstrual cramps cause painful bowel motions.
It’s important to note that a woman’s pain level isn’t always proportionate to the severity of her illness.
Some women with severe endometriosis experience no symptoms, while others with a milder form of the disease may experience significant pain or other symptoms.
Fertility and Endometriosis
Endometriosis affects between 20 and 40% of infertile women. Endometriosis is hypothesized to disrupt fertility in two ways: first, by distorting the fallopian tubes, preventing them from picking up the egg after ovulation, and second, by causing inflammation that can affect the function of the ovary, egg, fallopian tubes, or uterus. For additional care and support, consult a fertility professional.
Endometriosis risk factors
These variables greatly enhance your chances of developing this condition:
- Family tree.
- Late pregnancy.
- Women who have an uncommon uterus.
- There are no kids.
- Menstrual cycles that continue for more than seven days.
- Menstrual cycles are short.
Diagnosis of Endometriosis
If you are experiencing painful periods, do not be afraid to seek medical attention.
A gynecologist will review your medical history, perform a pelvic examination, and order any necessary, additional tests. Here are a few basic techniques to relieve endometriosis pain:
- Rest, relax, and meditate.
- Take warm baths.
- Prevent constipation.
- Get frequent exercise.
- Apply a hot water bottle or a heating pad to your abdomen.